In our last blogs, we get to know about, what 3D printing is, the steps involved in 3D printing, and what is an STL file, we learn about the different types of 3D printers, read the history of our 3D printers, know about different types of file formats that were used for our 3D printers, and learn what is SLA and DLP 3D printers.
Now in this blog, we will know about the difference between SLA v/s DLP 3D printing.
So, let’s get deep down into it…
SLA v/s DLP 3D Printer

[Credit – 3D Native]
SLA (Stereolithography) and DLP (Digital Light Processing) are two different types of 3D printing technologies that utilize light to cure liquid resin into solid objects layer by layer. While they share some similarities, they also have distinct differences in terms of how they work and the applications they are best suited for.
SLA (Stereolithography):
● Process: In SLA, a laser or a projector is used to selectively cure a liquid resin layer by layer. The build platform is lowered into the resin tank after each layer is cured, allowing the object to gradually rise out of the resin.
● Light Source: SLA can use laser-based or UV light-based systems to cure the resin. A laser is often more precise, allowing for fine details.
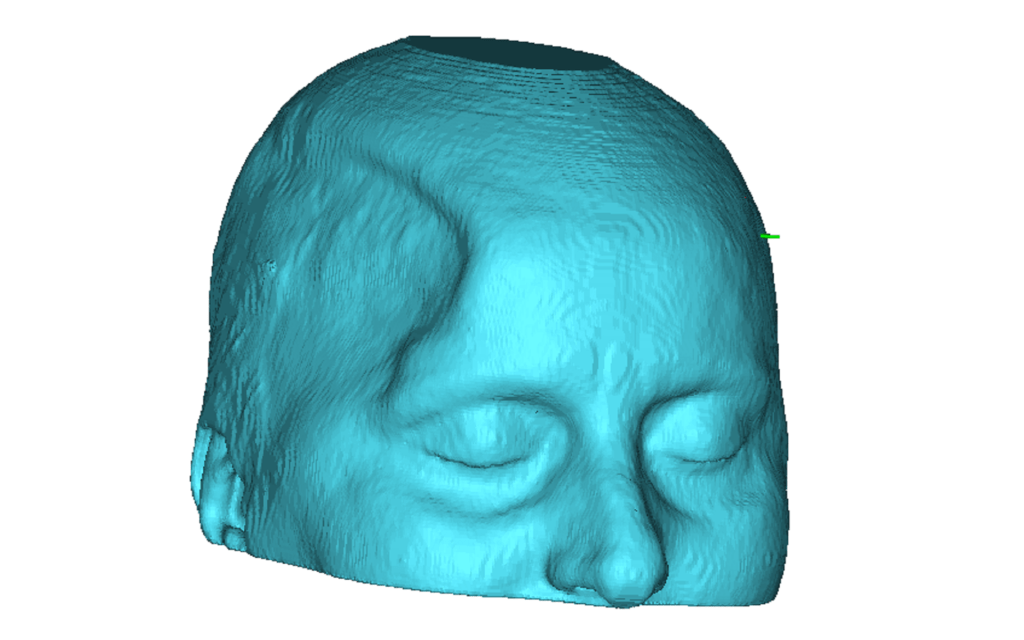
● Precision and Detail: SLA is generally known for its high precision and ability to produce intricate, detailed objects with smooth surfaces. It is commonly used for producing prototypes, jewelry, dental models, and other applications that demand high resolution.
● Speed: SLA can be slower compared to some other 3D printing technologies due to the need to cure each layer with a precise light source.
● Cost: SLA printers tend to be more expensive than some other 3D printing technologies due to their precision and the quality of output they can achieve.

[Source – Formlabs]
DLP (Digital Light Processing):
● Process: DLP uses a digital light projector to flash an entire layer of the object at once onto the liquid resin. The entire layer is cured simultaneously, which can make the printing process faster compared to SLA.
● Light Source: DLP uses UV light from a digital projector, exposing the entire layer in a single shot, which increases the speed of the process.
● Precision and Detail: While DLP can produce highly detailed objects, the level of detail might not be as fine as what SLA can achieve, particularly for objects with very small features.
● Speed: DLP is generally faster than SLA due to the simultaneous exposure of entire layers.
● Cost: DLP printers can often be more affordable than high-end SLA printers, making them a popular choice for users who need decent detail but also want relatively faster printing speeds.
In summary, SLA and DLP are both resin-based 3D printing technologies that utilize light to cure liquid resin, but they have differences in terms of precision, speed, cost, and the type of light exposure. The choice between the two largely depends on the specific requirements of the project, such as the level of detail needed, printing speed, and budget constraints.
Difference Between Materials of SLA and DLP 3D printers
SLA (Stereolithography) and DLP (Digital Light Processing) are both resin-based 3D printing technologies that use similar principles to cure liquid resin into solid objects using light. While the core material used in both technologies is resin, there are some differences in the types of resins and how they might be formulated for each process. Here are the key differences in the materials used in SLA and DLP printers:
1. Liquid Resin Formulation:
● SLA: SLA resins are often formulated to be sensitive to a specific wavelength of light, typically in the ultraviolet (UV) range. They need to be compatible with the specific wavelength of the laser used in SLA printers.
● DLP: DLP resins are also formulated to be sensitive to specific wavelengths of light, typically UV light emitted by digital projectors. The entire layer of the object is cured at once, requiring the resin to respond uniformly to light exposure.
2. Curing Mechanism:
● SLA: In SLA, a laser or UV light is precisely directed onto the resin surface, curing it point by point or in small regions.
● DLP: DLP exposes the entire layer to light simultaneously using a digital projector, curing the entire layer at once. This can lead to slightly different curing characteristics compared to SLA.
3. Printing Speed and Layer Thickness:
● SLA: SLA printers can offer very fine layer resolutions and high levels of detail but can be slower due to the point-by-point curing process.
● DLP: DLP printers are often faster due to their ability to cure entire layers at once. This speed advantage can sometimes come at the cost of slightly reduced detail compared to SLA.
4. Resin Compatibility:
● SLA: SLA printers might have specific resin formulations optimized for their lasers or light sources. Interchanging resins between different SLA printers might require adjustments or compatibility checks.
● DLP: DLP printers can often accommodate a wider range of resins since they rely on a digital projector for light exposure, which can be adjusted to match different resin formulations.
5. Application Focus:
● SLA: SLA printers might have specific resin formulations optimized for their lasers or light sources. Interchanging resins between different SLA printers might require adjustments or compatibility checks.
● DLP: DLP printers can often accommodate a wider range of resins since they rely on a digital projector for light exposure, which can be adjusted to match different resin formulations.
6. Specialized Resins:
- Both SLA and DLP technologies offer a range of specialized resins designed for specific purposes, such as dental, castable, flexible, high-temperature, and engineering resins.
The primary distinction between the materials used in SLA and DLP printers lies in the curing mechanism, printing speed, and the specific requirements of each technology. While they both use liquid resins that solidify upon light exposure, the curing methods and application focus of each technology can result in some differences in the formulation and characteristics of the resins used.
Thank you, for being with us till here, now I think you understand the difference between SLA v/s DLP 3D printers.
In the next blog, we are going to know about the SLS 3D printer.
So, till then keep being awesome and keep learning, We will meet again in our next blog.