In our last blogs, we get to know about, what 3D printing is, the steps involved in 3D printing, and what is an STL file, we learn about the different types of 3D printers, we read the history of our 3D printers, and get to know about different types of file formats that were used for our 3D printers.
Now in this blog, we will learn about SLA 3D printers.
So, let’s get deep down into it…
Different Types of 3D Printers
There are various types of 3D printers available in the market, which printer you have to use has to be decided by you according to your work need. Here we will discuss all the various 3D printers available, and try to present you with a guide map, that will help you better understating the types of printers.
SLA [Stereolithography] Printer
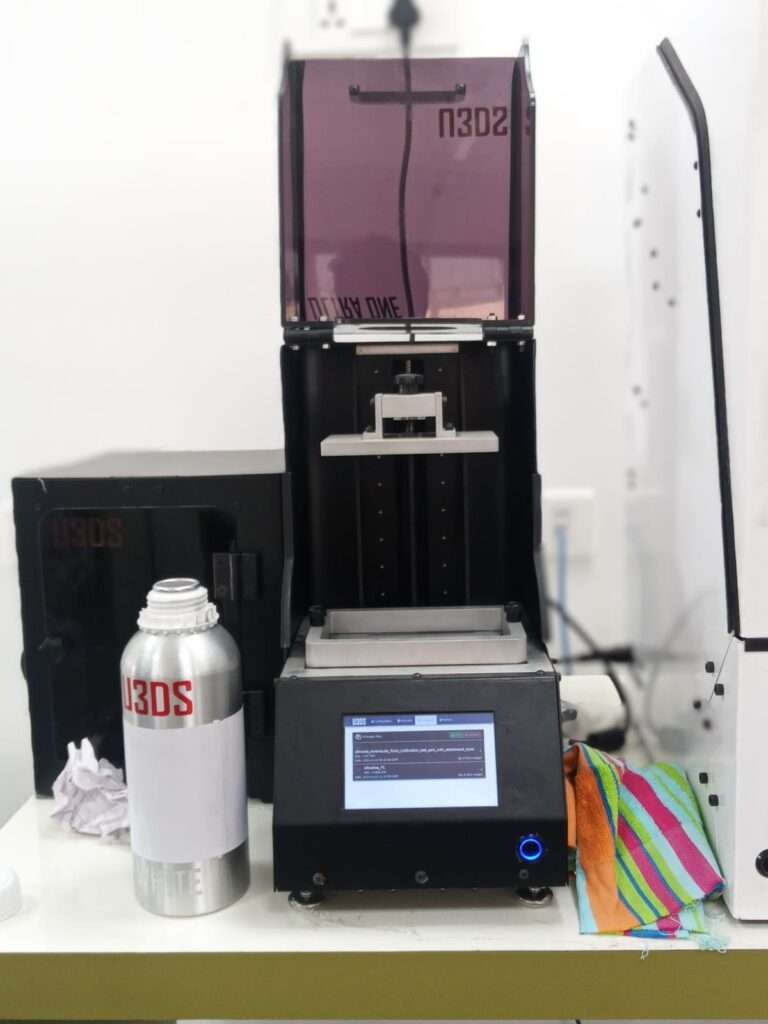

SLA stands for Stereolithography, and it’s a type of 3D printing technology that uses photopolymerization to create three-dimensional objects. SLA is one of the earliest and most widely used additive manufacturing processes, particularly for producing high-quality prototypes, intricate models, and parts with fine details.
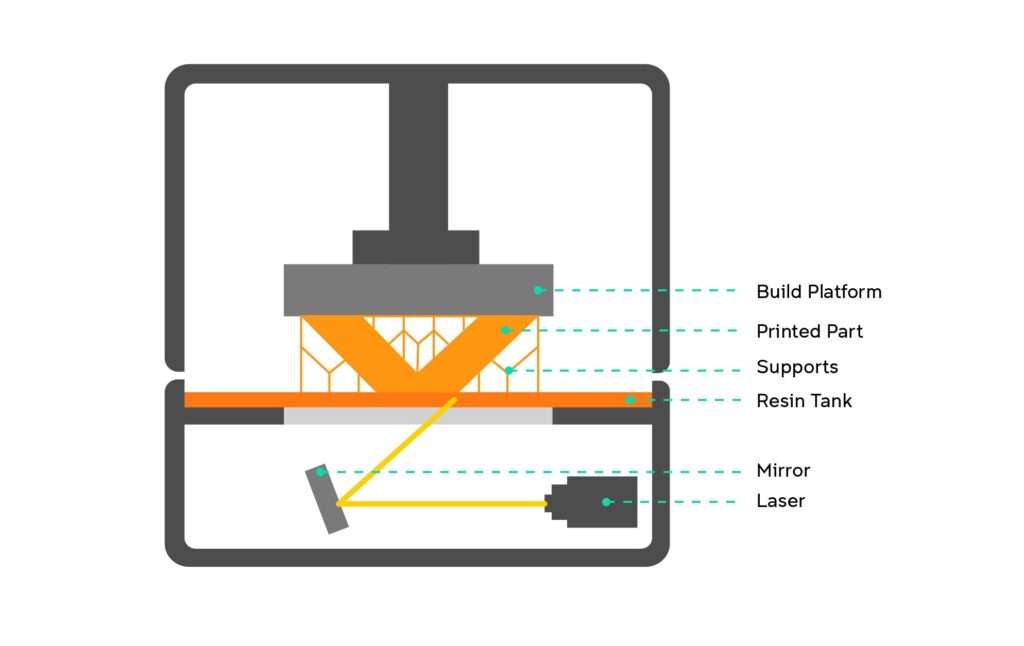
[Source – UNSW S Y D N E Y]
Here’s how an SLA 3D printer works:
- Resin Material: In SLA printing, a liquid photopolymer resin is used as the printing material. This resin is sensitive to certain wavelengths of light, usually ultraviolet (UV) light.
- Layer-by-Layer Printing: The 3D printing process begins with a 3D model designed using computer-aided design (CAD) software. The model is then sliced into thin horizontal layers using slicing software, just like in other 3D printing methods.
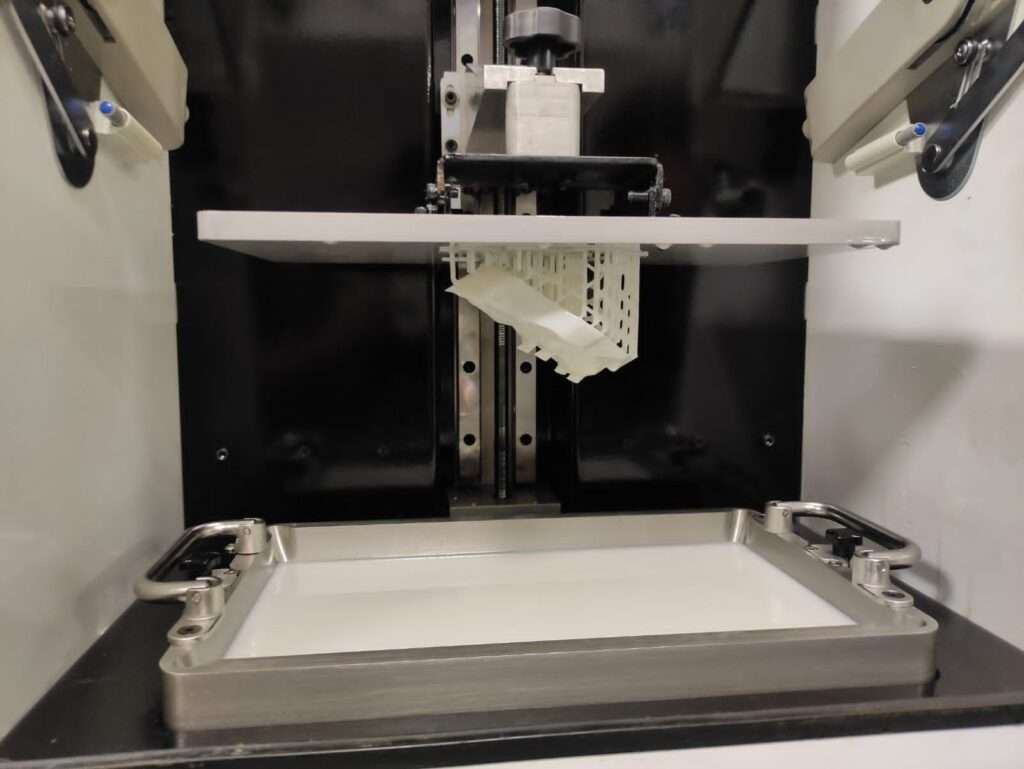
- Building the Object: The SLA printer’s build platform is submerged in a tank of the liquid resin. A UV laser or a light projector is then used to selectively cure (solidify) the resin layer by layer. The UV light is projected onto the resin’s surface according to the cross-section of the sliced model, solidifying the resin where the light touches.
- Platform Movement: As each layer is cured, the build platform moves slightly upward, allowing the next layer of liquid resin to flow over the previously cured layer. The process continues, layer by layer until the entire object is complete.
- Support Structures: In some cases, support structures may be required to ensure overhanging parts of the model are properly supported during the printing process. These supports are also made of the same resin and are generated by the slicing software.
- Post-Processing: Once the printing is complete, the object is removed from the resin tank. It may need additional post-processing steps such as cleaning to remove excess resin, and in some cases, curing under additional UV light to ensure the material’s final properties.
Advantages of SLA 3D Printing:
- High Detail: SLA is known for producing highly detailed and intricate parts with smooth surfaces.
- Wide Material Range: Different types of photopolymer resins are available, including those with varying mechanical properties, colors, and even transparent or flexible materials.
- Accuracy: SLA printers are capable of achieving high dimensional accuracy and fine features.
- Complex Geometries: SLA can handle complex geometries, including overhangs and delicate structures.
- Smooth Finish: Parts printed using SLA often have a smooth finish right out of the printer.
Limitations of SLA 3D Printing:
- Material Properties: The mechanical properties of SLA parts might not be as robust as those produced using other technologies like FDM or SLS.
- Build Size: The build volume of SLA printers can be limited compared to some other 3D printing technologies.
- Post-Processing: SLA prints usually require post-processing to remove excess resin and achieve the desired mechanical properties.
SLA 3D printing is commonly used in industries like jewelry, dentistry, rapid prototyping, and small-scale production of highly detailed parts. It has played a significant role in advancing 3D printing technology and applications.
Material used in SLA
There are various types of SLA resins available, each tailored to different applications and requirements. Here are some common types of SLA resins:
- Standard Resins: These are versatile resins suitable for a wide range of applications. They come in different colors and offer a good surface finish and detail resolution. Standard resins are often used for prototyping, concept modeling, and aesthetic designs.
- Engineering Resins: These resins are formulated to offer enhanced mechanical properties, making them suitable for functional prototypes and end-use parts. Engineering resins can include tough, durable, and high-temperature-resistant variants.

Source – Meridian product corporation
- Flexible Resins: Flexible resins produce parts with rubber-like flexibility and elasticity. They are often used to create gaskets, seals, wearable prototypes, and objects requiring impact resistance.
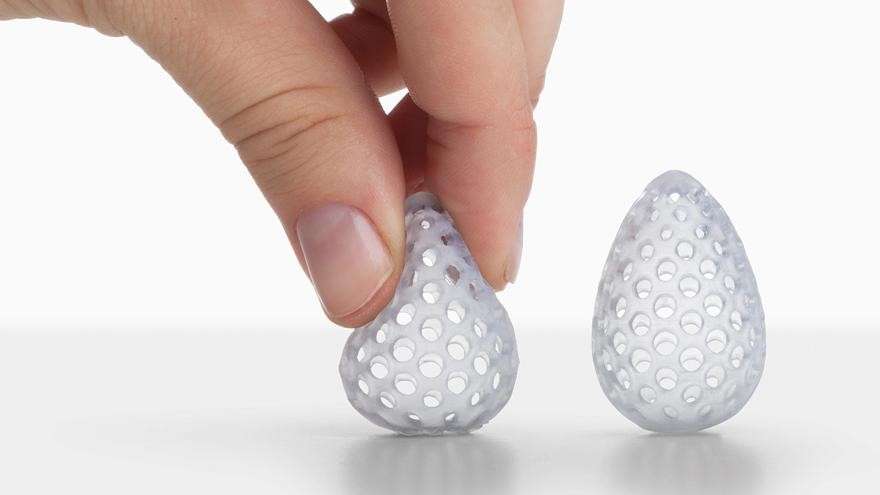

Source – Core77
- Transparent Resins: These resins are designed to produce transparent or translucent parts with optical clarity. They find applications in creating clear prototypes, lenses, light guides, and models that require light transmission.

Source – Formlabs
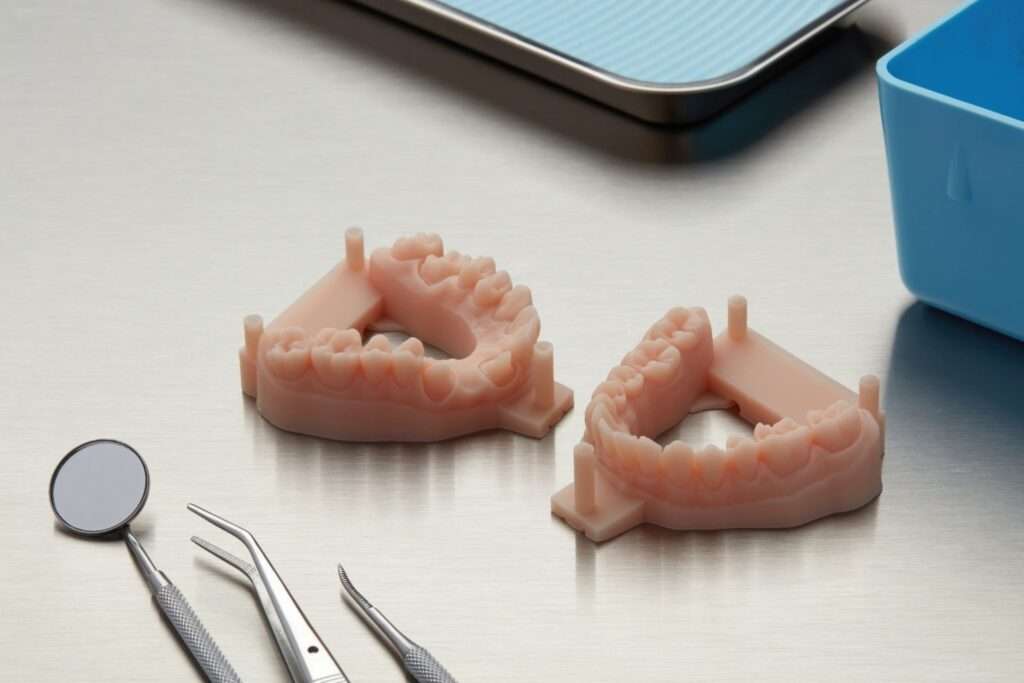
- Dental and Medical Resins: Specialized resins for dental and medical applications have been developed. These resins are biocompatible and safe for use in dental models, surgical guides, orthodontic devices, and more.

- Castable Resins: Castable resins are used for creating intricate models that can be used in investment casting processes. They burn out cleanly during the casting process, leaving behind voids that can be filled with molten metal.
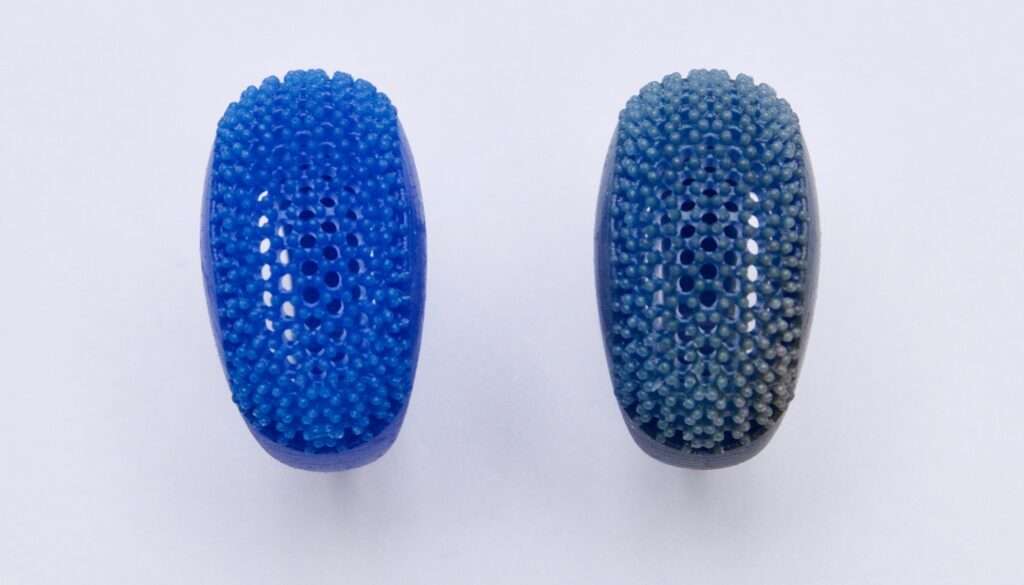

Source – Formlabs
- High-Detail Resins: These resins are optimized for achieving extremely fine details and smooth surfaces. They are used for creating miniatures, jewelry, figurines, and other objects requiring intricate details.
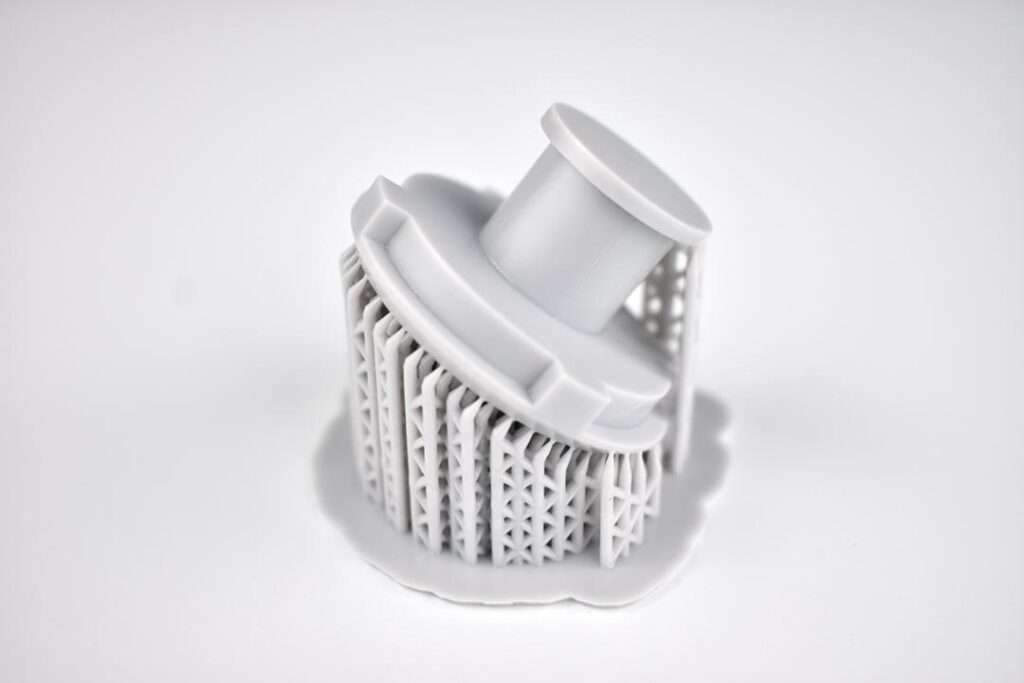

Source – MakeitQuick
It’s important to note that SLA resins are typically specific to the manufacturer’s printer and may require different printing settings and post-processing techniques. Additionally, some resins may require proper handling, ventilation, and curing to achieve the desired material properties.
When choosing an SLA resin, it’s essential to consider factors such as mechanical properties, surface finish, color options, and the intended application of the printed object. Always refer to the manufacturer’s recommendations and guidelines for using specific resins with your SLA 3D printer.
Thank you, for being with us till here, now I think you understand the SLA 3D printer, and get an idea about the resins used for printing
In the next blog, we are going to learn about the DLP 3D printer.
So, till then keep being awesome and keep learning, We will meet again in our next blog.
